Java8新特性 - Stream流的应用
😄生命不息,写作不止
🔥 继续踏上学习之路,学之分享笔记
👊 总有一天我也能像各位大佬一样
🏆 一个有梦有戏的人 @怒放吧德德
🌝分享学习心得,欢迎指正,大家一起学习成长!
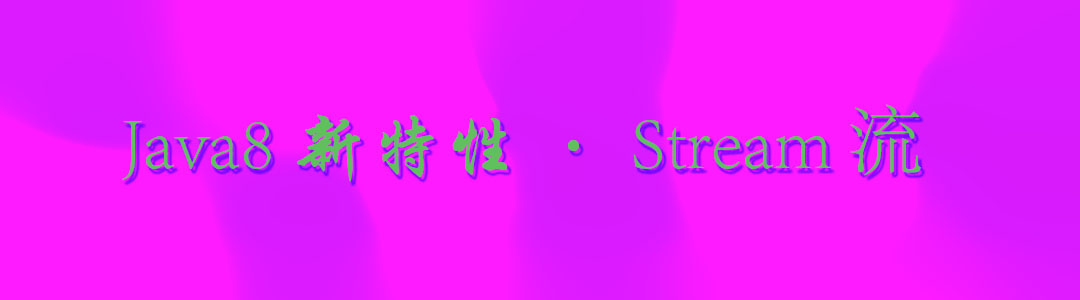
简介
stream是java8新出的抽象概念,他可以让你根据你期望的方式来处理集合数据,能够轻松的执行复杂的查找、过滤和映射数据等操作。Stream 使用一种类似用 SQL 语句从数据库查询数据的直观方式来提供一种对 Java 集合运算和表达的高阶抽象。
Stream API可以极大提高Java程序员的生产力,让程序员写出高效率、干净、简洁的代码。这种风格将要处理的元素集合看作一种流, 流在管道中传输, 并且可以在管道的节点上进行处理, 比如筛选, 排序,聚合等。
元素流在管道中经过中间操作(intermediate operation)的处理,最后由最终操作(terminal operation)得到前面处理的结果。
对于一个集合,首先需要转成stream流,可以使用中间操作(filter过滤器、distinct去重、sorted排序等),但是最后是由终止操作结束(forEach遍历、collect转换、min,max最小最大等)。
Stream流的使用
生成流
在 Java 8 中, 集合接口有两个方法来生成流:
- stream() − 为集合创建串行流,也就是采用单线程执行
- parallelStream() − 为集合创建并行流,也就是采用多线程执行
串行流:单线程的方式操作, 数据量比较少的时候使用
并行流:多线程方式操作,数据量比较大的时候使用
主要原理是:将一个大的任务拆分n多个小的子任务并行执行,
最后在统计结果,有可能会非常消耗cpu的资源,确实可以
提高效率,但是在数据量不多的时候就不要使用并行流。
Stream将list转换为Set
首先将list转成stream流,在通过collect(Collectors.toSet())的方法得到set集合。但是,直接这么操作,set集合是无法去重的。首先需要了解一下set的底层是如何防止重复的key的,我们都知道set底层依赖map防止重复的key,map集合底层依靠equals比较防止重复的key。所以我们需要在实体类型中去重写equals和hashcode的方法。
实体类:
package com.jdk8.demo.lambda.entity;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author: lyd
* @description: 实体
* @Date: 2022/10/5
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer score;
// ... 省略get、set、构造方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Student) {
return name.equals(((Student) obj).name) && score == ((Student) obj).score;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return score.hashCode();
}
}
测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Stream将list转换为Set
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student(\"lyd\", 99));
students.add(new Student(\"lkj\", 55));
students.add(new Student(\"llm\", 67));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
/**
* set底层依赖map防止重复的key,map集合底层依靠equals比较防止重复的key
*/
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
Set<Student> collect = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
Iterator<Student> iterator = collect.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Student next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next.getName() + \" -> \" + next.getScore());
}
}
结果:

Stream将list转换为Map
list集合转成stream流之后,通过<R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector),在通过
Collector<T, ?, Map<K,U>> toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T, ? extends U> valueMapper) {
return toMap(keyMapper, valueMapper, throwingMerger(), HashMap::new);
}
来声明key和value。如下代码,可以这么理解,stream.collect(Collectors.toMap(key, value)),key和value都是通过new Function<T, K>,对于key:T指的是Steam流的类型(既Student),而K代表的是map中的key值,因此这里是String类型的,在apply方法中去返回key值,通过student的名字来最为key,因此这里返回student.getName()。而第二个作为map的value,整体操作也是跟key差不多,主要还是需要注意的是,value存的是student,因此需要使用Student类型。
Map<String, Student> map = stream.collect(Collectors.toMap(new Function<Student, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Student student) {
return student.getName();
}
}, new Function<Student, Student>() {
@Override
public Student apply(Student student) {
return student;
}
}));
最后都可以使用lambda表达式来
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Stream将list转换为Map
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student(\"lyd\", 99));
students.add(new Student(\"lkj\", 55));
students.add(new Student(\"llm\", 67));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
Map<String, Student> map = stream.collect(Collectors.toMap(student -> student.getName(), student -> student));
map.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(\"key: \" + key + \" -> value: \" + value));
}
结果
Stream使用Reduce求和
通过使用stream的reduce方法,在里面去new BinaryOperator,代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Stream使用Reduce求和
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student(\"lyd\", 99));
students.add(new Student(\"lkj\", 55));
students.add(new Student(\"llm\", 67));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
Optional<Student> sum = stream.reduce((student, student2) -> {
Student sum1 = new Student(\"sum\", student.getScore() + student2.getScore());
return sum1;
});
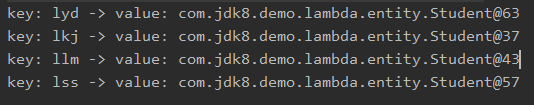
System.out.println(sum.get().getName() + \" : \" + sum.get().getScore());
}
结果

Stream使用Max和Min
实际上就是通过匿名内部类new Comparator()实现public int compare(Student o1, Student o2)比较方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// StreamMax和Min
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student(\"lyd\", 99));
students.add(new Student(\"lkj\", 55));
students.add(new Student(\"llm\", 67));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
Optional<Student> max = stream.max((o1, o2) -> o1.getScore() - o2.getScore());
System.out.println(max.get().getScore());
Stream<Student> stream2 = students.stream();
Optional<Student> min = stream2.min((o1, o2) -> o1.getScore() - o2.getScore());
// 可以使用方法引入更加简便
// Optional<Student> min = stream2.min(Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getScore));
System.out.println(min.get().getScore());
}
结果
Stream中Match匹配
- anyMatch表示,判断的条件里,任意一个元素成功,返回true
- allMatch表示,判断条件里的元素,所有的都是,返回true
- noneMatch跟allMatch相反,判断条件里的元素,所有的都不是,返回true
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student(\"lyd\", 99));
students.add(new Student(\"lkj\", 55));
students.add(new Student(\"llm\", 67));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
boolean allMatch = stream.allMatch(student -> student.getScore() > 60);
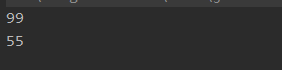
System.out.println(\"allMatch: \" + allMatch);
Stream<Student> stream2 = students.stream();
boolean anyMatch = stream2.anyMatch(student -> student.getScore() > 60);
System.out.println(\"anyMatch: \" + anyMatch);
Stream<Student> stream3 = students.stream();
boolean noneMatch = stream3.noneMatch(student -> student.getScore() > 60);
System.out.println(\"noneMatch: \" + noneMatch);
}
结果

Stream的过滤与遍历
stream的过滤是通过filter方法,通过实现匿名内部类new Predicate()的test方法,并且可以使用链式编程,持续过滤并且遍历,因为过滤不是终止运算。然而forEach是实现匿名内部类new Consumer()的accept方法。可以通过new的方式在通过idea来生成lambda表达式。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student(\"lyd\", 99));
students.add(new Student(\"lkj\", 55));
students.add(new Student(\"llm\", 67));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
stream.filter(student -> student.getName() != null)
.filter(student -> student.getScore() > 70)
.forEach(student -> System.out.println(\"name: \" + student.getName() + \" score: \" + student.getScore()));
}
结果

Stream的排序
不仅Arrays以及数组能够实现排序甚至是重写排序规则,Stream流也是提供了相应的方法。通过实现匿名内部类Comparator的compare方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student(\"lyd\", 99));
students.add(new Student(\"lkj\", 55));
students.add(new Student(\"llm\", 67));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
stream.sorted(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getScore() - o2.getScore();
}
}).forEach(new Consumer<Student>() {
@Override
public void accept(Student student) {
System.out.println(\"name: \" + student.getName() + \" score: \" + student.getScore());
}
});
/*lambda*/
stream.sorted((o1, o2) -> o1.getScore() - o2.getScore())
.forEach(student -> System.out.println(\"name: \" + student.getName() + \" score: \" + student.getScore()));
/*方法引入*/
stream.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getScore))
.forEach(student -> System.out.println(\"name: \" + student.getName() + \" score: \" + student.getScore()));
}
结果
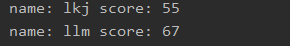
Stream的limit与skip
在SQL中可以通过limit进行分页数据的获取,在java8的stream流中,limit是获取集合中的前几个值,而skip是跳过几个元素。当我们需要获取第二到第三个元素的时候,可以通过skip(1)在通过limit(2)获取。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student(\"lyd\", 99));
students.add(new Student(\"lkj\", 55));
students.add(new Student(\"llm\", 67));
students.add(new Student(\"lss\", 87));
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
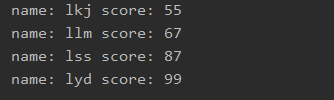
stream.skip(1).limit(2).forEach(student -> System.out.println(\"name: \" + student.getName() + \" score: \" + student.getScore()));
}
结果
工作繁忙也需要学习。
👍创作不易,如有错误请指正,感谢观看!记得点赞哦!👍
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/lyd-code/p/16774142.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园