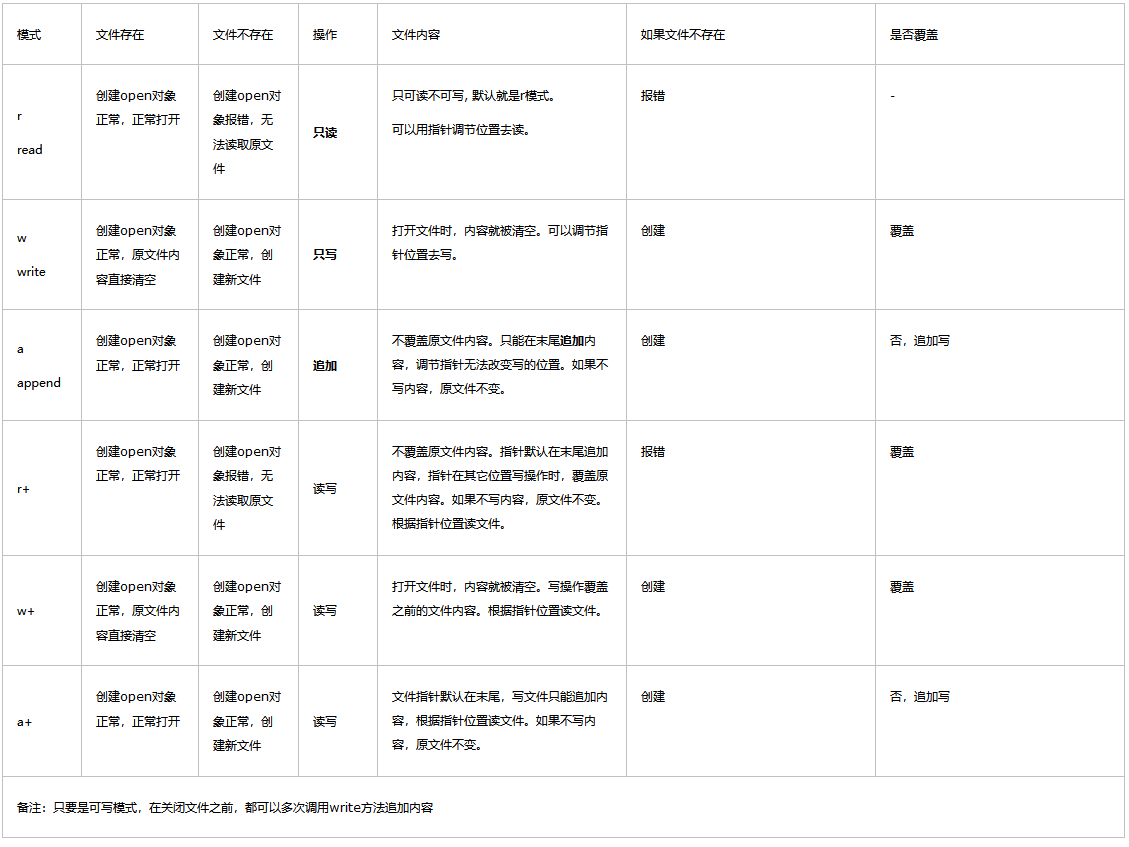
文件操作的模式
文件操作的模式如下表:
1. open 打开文件
使用 open 打开文件后一定要记得调用文件对象的 close() 方法。比如可以用 try/finally 语句来确保最后能关闭文件。
file_object = open(r\'D:\\test.txt\') # 打开文件
try:
all_the_text = file_object.read( ) # 读文件的全部内容
finally:
file_object.close( ) # 关闭文件
print(all_the_text)
注:不能把 open 语句放在 try 块里,因为当打开文件出现异常时,文件对象 file_object 无法执行 close() 方法。
2. 读文件
读文本文件方式打开文件
file_object = open(r\'D:\\test.txt\', \'r\') # 打开文件
#第二个参数默认为 r
file_object = open(r\'D:\\test.txt\') # 打开文件
读二进制文件方式打开文件
file_object= open(r\'D:\\test.txt\', \'rb\') # 打开文件
读取所有内容
file_object = open(r\'D:\\test.txt\') # 打开文件
try:
all_the_text = file_object.read( )# 读文件的全部内容
finally:
file_object.close( ) # 关闭文件
print(all_the_text)
读固定字节
file_object = open(r\'D:\\test.txt\', \'rb\') # 打开文件
try:
while True:
chunk = file_object.read(100) # 读文件的100字节
if not chunk:
break
#do_something_with(chunk)
finally:
file_object.close( ) # 关闭文件
读每行 readlines
file_object = open(r\'D:\\test.txt\', \'r\') # 打开文件
list_of_all_the_lines = file_object.readlines( ) #读取全部行
print(list_of_all_the_lines)
file_object.close( ) # 关闭文件
如果文件是文本文件,还可以直接遍历文件对象获取每行:
file_object = open(r\'D:\\test.txt\', \'r\') # 打开文件
for line in file_object:
print(line)
file_object.close( ) # 关闭文件
3. 写文件
写文本文件方式打开文件
file_object= open(\'data\', \'w\')
写二进制文件方式打开文件
file_object= open(\'data\', \'wb\')
追加写文件方式打开文件
file_object= open(\'data\', \'w+\')
写数据
\'\'\'
学习中遇到问题没人解答?小编创建了一个Python学习交流群:711312441
寻找有志同道合的小伙伴,互帮互助,群里还有不错的视频学习教程和PDF电子书!
\'\'\'
all_the_text=\"aaa\\nbbb\\nccc\\n\"
file_object = open(r\'D:\\thefile.txt\', \'w\') # 打开文件
file_object.write(all_the_text) #写入数据
file_object.close( ) # 关闭文件
写入多行
all_the_text=\"aaa\\nbbb\\nccc\\n\"
file_object = open(r\'D:\\thefile.txt\', \'w\')# 打开文件
file_object.writelines(all_the_text) #写入数据
file_object.close( ) # 关闭文件
追加
file = r\'D:\\thefile.txt\'
with open(file, \'a+\') as f: # 打开文件
f.write(\'aaaaaaaaaa\\n\')
判断文件是否存在:
import os.path
if os.path.isfile(\"D:\\\\test.txt\"): # 判断文件是否存在
print(\":\\\\test.txt exists\")
import os
os.getcwd() # 获得当前目录
os.chdir(\"D:\\\\test.txt\") # 改变当前目录
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/python1111/p/16630800.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园